1.3 Given a scenario, set up and configure accessories and ports of mobile devices.
- Connection Methods
- Universal Serial Bus (USB/USB-C/microUSB/miniUSB)
- Lighting
- Serial Interfaces
- Near-Field Communication (NFC)
- Bluetooth
- Hotspot
- Accessories
- Touch Pens
- Headsets
- Speakers
- Webcam
- Docking Station
- Port Replicator
- Trackpad / Drawing Pad
Connection Types for a Mobile Device – Wired
Note that there are many more types of USB connectors (Type A vs Type B connectors, and USB 1.0/2.0 vs 3.0 connectors). We will look at these in more detail in a later section.


The standard USB connector is Type-A
You can purchase a cable in any of the above models that is Type B, USB-C, Lightning, etc. on one side, and Type A on the other.
Connect the Type A side to a computer (to transfer data) or to a power adapter (to charge the mobile device).
Connection Types for a Mobile Device – Wireless
There are many ways to wirelessly connect our mobile device. What are they?
| NFC | Near-Field Communication Uses an electromagnetic signal generated by a loop antenna inside the mobile device NFC Devices work together automatically. We don’t have to program them. Uses Contactless payments/Mobile payments (your mobile device can act as a credit card or a debit card) Key card (your mobile device can act as a key card in an office building or hotel) Sharing data between mobile devices Range of 4cm (approx. 2 inches) (maximum) |
| Bluetooth | Uses radio waves to connect peripherals and transfer data Devices must “pair” with each other before any data can transfer over Bluetooth Uses Connect your phone to a headset Connect your phone to a vehicle audio system Transfer files between devices Range of 100m There is also a Bluetooth Low Energy, which uses less battery life but has slower transfer speeds. It also has a range of 100m. |
| IR | Infrared Uses invisible light to transfer data between devices The devices must be aligned so that their IR transmitters/receivers have a clear line of sight Uses Transfer data between devices IR was popular around 2010, but currently few mobile devices have IR capabilities |
| Hotspot | When you set up a hotspot, your mobile device broadcasts a Wi-Fi signal (acts like a wireless access point) Other devices can connect to it and share its internet connection Uses Provide a wireless internet connection to a laptop, phone, tablet, or other device Useful when travelling with a laptop and unable to find an internet connection Range of 100m, but depends on mobile device and interference from walls, buildings, and other obstruction |
Phone Accessories
A wide range of phone accessories are available
Phone accessories connect via
- USB/lighting (very common)
- Bluetooth (very common)
- Headphone jack (common for headphones, and less common for other devices). Many device manufacturers are removing the headphone jack. Some people think that the headphone jack delivers poor sound quality compared to Bluetooth.
- Apple Airpods use Bluetooth to communicate with non-Apple devices, but they use a proprietary communication protocol to communicate with Apple devices.
- Apple Airpods use Bluetooth to communicate with non-Apple devices, but they use a proprietary communication protocol to communicate with Apple devices.
- Internet (Wi-Fi/cellular data) (the phone and device share data through an external server – this is not a common method)
A wireless accessory will usually contain a USB port for charging, or will contain batteries





Docking Station vs Port Replicator
- A docking station allows a user to connect his laptop to many devices at the same time via one cable.
- It is ideal for an office worker who takes his laptop to and from work every day. At work, the user wants to connect external monitors, ethernet, and USB devices such as mice, keyboards, and printers, but wants to avoid the hassle of connecting each device manually
- The peripherals connect to the docking station, and the docking station connects to the laptop.
- Only “business-grade” laptops have docking ports. The docking port is located on the bottom or right of the laptop.
- The docking station may have
- A button to power the laptop on or off
- A button to eject the laptop from the dock
- A button to lock/unlock the laptop in the dock
- A docking station is typically proprietary to the manufacturer, although aftermarket docking stations exist. A docking station may work with multiple models of laptops made by the same manufacturer
- Older docking stations can have optional slots to add memory, hard disk drives, and PCI cards, which the laptop can take advantage of when it is connected. These are not popular.
- Disadvantages
- Some of the docks’ ports contain pins that are easily damaged if the laptop isn’t inserted correctly
- Dock may take up too much space on the desk
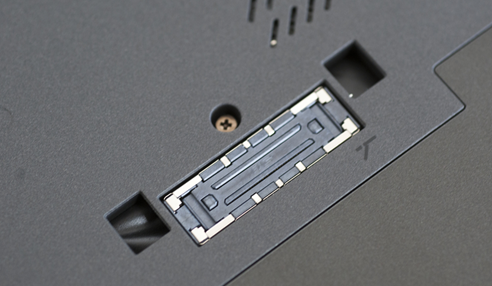
Older models of docking stations look like this

Back of Dock

Docking port on bottom of laptop
Newer docking stations use USB-C
- The user connects the USB-C cable to the laptop
- All data and power are transmitted through the USB-C cable
- Some docking stations require two connections to the laptop (one for the peripherals and one for power)
- Most laptops with USB-C ports (even consumer-grade laptops) can function with the newer docking stations. That is because the drivers for the peripherals are separate from the dock. The dock is passing the data through to the peripherals.

What’s the difference between a port replicator and a docking station?
- Technically a port replicator includes the same ports that are on the laptop
- A docking station includes additional ports that aren’t found on the laptop (for example a serial port)
- A docking station may have additional hardware support
Trackpad / Drawing Pad
There are several alternatives to using a mouse


