1.4 Given a scenario, use the appropriate Microsoft Windows 10 Control Panel utility
- Internet Options
- Devices and Printers
- Programs and Features
- Network and Sharing Center
- System
- Windows Defender Firewall
- Sound
- User Accounts
- Device Manager
- Indexing Options
- Administrative Tools
- File Explorer Options
- Show Hidden Files
- Hide Extensions
- General Options
- View Options
- Power Options
- Hibernate
- Power Plans
- Sleep/Suspend
- Standby
- Choose What Closing the Lid Does
- Turn on Fast Startup
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) Selective Suspend
- Ease of Access
In Windows 10, you will find that you can change a setting from the Control Panel or from the Windows Settings panel. The Control Panel has more options than the settings panel.
Control Panel – Internet Options
Internet Options can be accessed from the Control Panel or from Internet Explorer (Microsoft Edge does not allow you to access Internet Options). Internet settings don’t apply to other web browsers (Google Chrome, Firefox, etc.). Internet Explorer is no longer supported. Many settings must now be changed directly from the web browser that you are using.
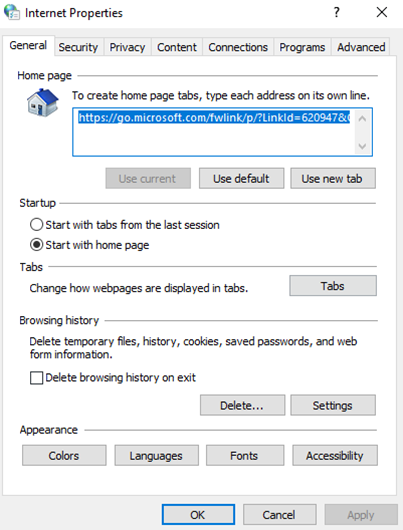
The General tab allows you to
- Set a homepage (the page that is displayed when you first open Internet Explorer)
- Allows you to modify the appearance of the browser.
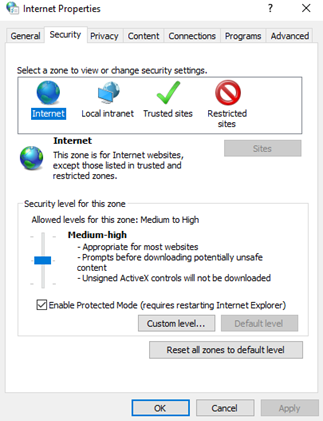
The Security tab allows you to set the security level for a website. There are four categories
- Internet: normal websites; Internet websites are normally not trusted
- Local Intranet: websites on the corporate network; Local Intranet websites are normally trusted
- Trusted sites: sites that are considered trusted. A user can add websites to the Trusted Sites list, even if it is an internet site.
- Restricted sites: sites that are not trusted. A user can add websites to the Restricted sites list, even if it is an intranet site
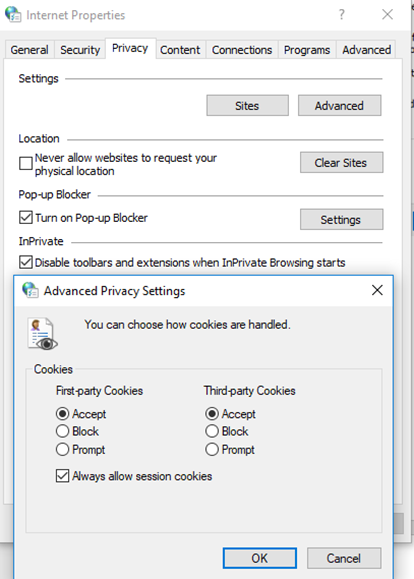
The Privacy tab allows you to set which websites can save cookies.
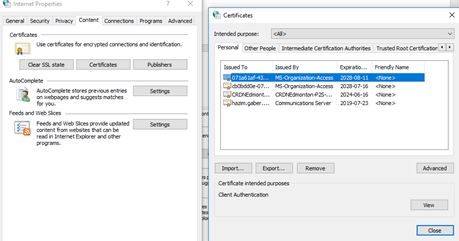
The Content tab lists all the certificates installed on the computer.
The Connections tab allows you to add and remove VPN connections.
The Programs tab lists the installed add-ons and plug-ins. Plug-ins provide additional functionality to Internet Explorer. This tab also allows you to set default programs for browsing the internet.
The Advanced tab allows to you to select advanced options such as Accessibility, script debugging, HTTP settings, and security settings.
Nobody uses (or should be using) Internet Explorer now, so forget all about this section.
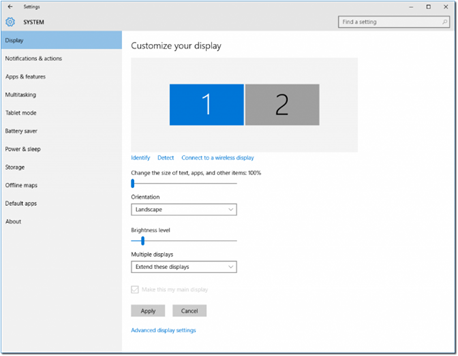
Control Panel – Display
Display settings allow you to
- Set the brightness (on a laptop screen)
- Set the scale (zoom)
- Set the screen resolution
- Windows will show you the recommended screen resolution
- The available screen resolutions depend upon the type of graphics card and monitor that you have
- Set the order of the displays (when there are multiple displays)
In advanced display settings, you can set the Refresh Rate. The refresh rate is the speed at which the screen updates (like frames per second).
- 60 Hz is the most common setting
- High-end graphics cards and monitors may offer higher refresh rates
- If we have multiple monitors, we can adjust their orientation
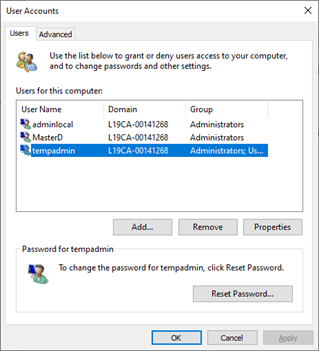
Control Panel – User Accounts
User Accounts lets you make add, remove, or disable user accounts that are present on your computer. changes to the accounts on your computer. You can choose whether an account is an administrator.
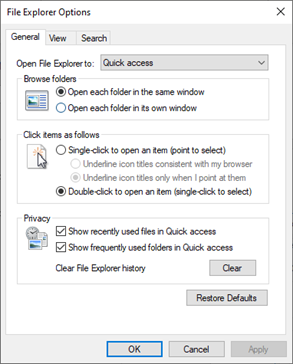
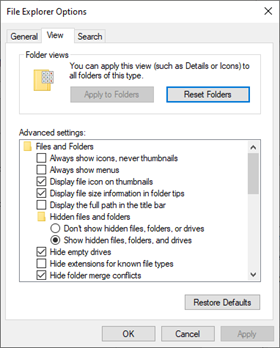
Control Panel – File Explorer Options
File Explorer Options (formerly Folder Options) allows you to control how files and folders are displayed
On the General Tab
- Choose whether to open new folders in the same window or in new windows
- Choose whether an item opens with a single-click or a double-click
- Ability to delete your history (File Explorer remembers the folders you recently visited)
On the View Tab you
- Can choose to show or hide hidden files and/or protected operating system files
- Can choose to show or hide other items such as the status bar, drive letters, file sizes, etc.
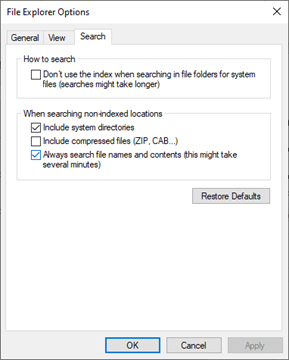
On the Search Tab
- Choose whether to use the search index (Windows creates an index of file names). Using the index makes the search faster, but less accurate, especially for slower computers.
- Choose whether to search directories that aren’t indexed
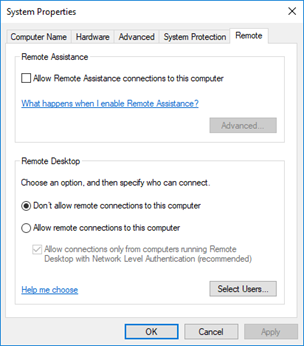
Control Panel – System (Performance, Remote, Protection)
In Windows 10, Performance is a separate utility. In older versions of windows, Performance is part of System Properties.
The remote tab allows remote access to the computer (via Remote Desktop). If you disable it, others may still be able to connect via third-party applications
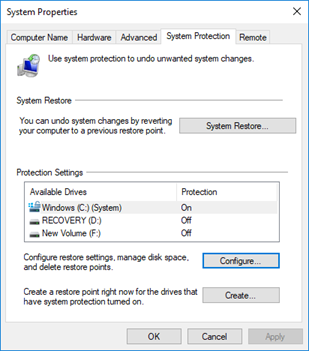
Protection allows you to enable/disable System Restore.
Control Panel – Power Options
Power Options allows you to choose how many minutes of inactivity are required until the computer goes to sleep / turns off the screen.
- Options vary between one minute and never
- You can have different settings for when the computer is on battery power and when it is plugged in
Advanced Power Options
- Choose what the power button does
- The computer can Sleep, Hibernate, Shut Down, Turn off the Display, or Do Nothing
- You can have different settings for when the computer is on battery and when it is plugged into a wall outlet
- Choose what closing the lid does (on a laptop)
- The computer can Sleep, Hibernate, Shut Down, or Do Nothing
- You can have different choices for when the computer is on battery and when it is plugged into a wall outlet
- Other settings
- Turn on fast start up (allows you to turn the computer on in a few seconds by saving some data to the hard disk)
- Choose whether Sleep, Hibernate, and Lock options are available
- Sleep is a “low power” mode. The computer is still running and will slowly drain the battery if not connected to a wall outlet.
- Hibernate forces the computer to shut down (but the contents of the RAM are saved to disk). When the computer starts back up, the contents of the RAM are reloaded back to memory and the computer resumes as before.
- Sleep is a “low power” mode. The computer is still running and will slowly drain the battery if not connected to a wall outlet.
- Turn on fast start up (allows you to turn the computer on in a few seconds by saving some data to the hard disk)
- Choose or customize a power plan
- You can customize additional settings for the computer hardware and limit how much power they consume when the computer is plugged in vs when it is on battery
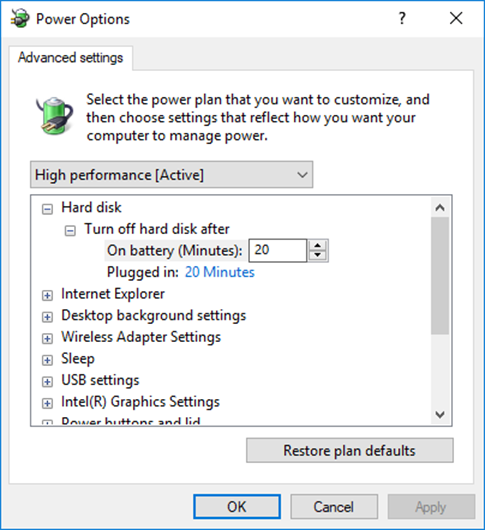
USB Selective Suspend is an option that allows Windows to shut off power to some of the USB drives. This allows the computer to conserve power by not powering unused ports
Control Panel – Programs and Features
Programs and Features allows you to view a list of installed programs and details such as
- Program name
- Program manufacturer
- Size of the program
- Date installed
You have the option to uninstall the program. You can only uninstall one program at a time. Some programs also provide the option to modify or repair the program’s installation.
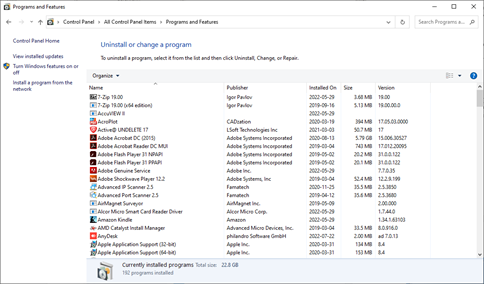
Under Optional Features it is possible to add or remove Windows features such as language packs, PowerShell, Virtualization Support, etc.
Control Panel – Devices and Printers
Devices and Printers shows us a list of installed printers and scanners. This information includes the name of each device and its status (Online, Offline, Disconnected).
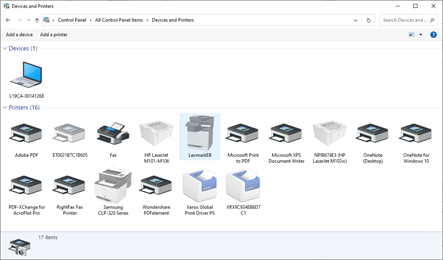
Some of the things we can do
- We can open a Print Queue. This shows documents that the printer will print, and their status.
- We can choose to Manage the printer. This allows us to edit the printer’s settings.
- We can choose to Remove a printer
- We can add a printer using a wizard (see previous section on printers).
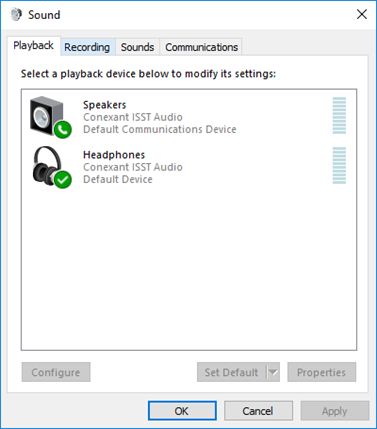
Control Panel – Sound
The Sound settings allow us to modify the sound settings.
Playback Tab
- The playback tab shows us a list of playback devices (speakers and headphones)
- We can choose to set one device as default
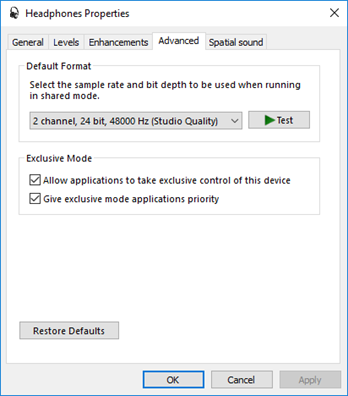
- We can double-click on a device to show its properties
- Enable/disable device
- Edit name
- Edit volume
- Edit audio quality
- Different types of devices have different properties
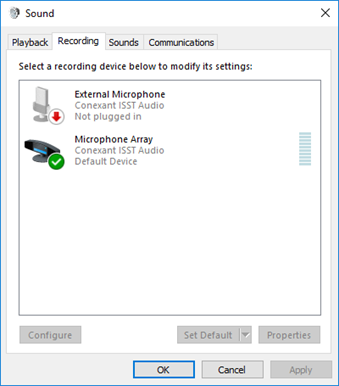
Recording Tab
- The recording tab shows a list of recording devices (microphones)
- We can double-click on a device to show its properties
- Enable/disable device
- Edit name
- Edit volume
- Edit audio quality
- Different types of devices have different properties
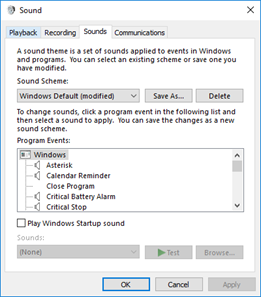
Sounds Tab
- The sounds tab allows you to modify the default Windows sounds for events (Critical Alert, Windows Login, etc.)
- We can choose a sound from a Windows library or record your own sound
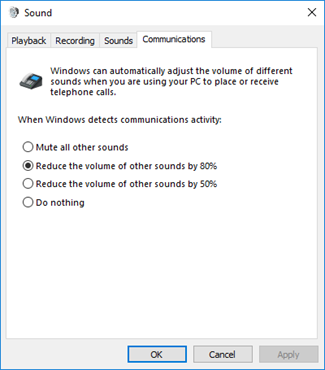
Communications Tab
- The communications tab allows Windows to reduce the volume of other sounds when it detects you making/receiving a phone call (for example, on Teams or Skype)
- Options are
- Mute sounds
- Reduce volume by 80%
- Reduce volume by 50%
- Do nothing
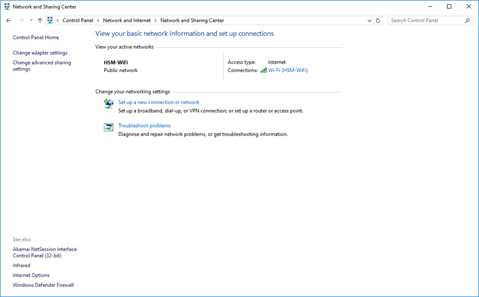
Control Panel – Network and Sharing Center
Network and Sharing Center shows the network or networks that the computer is currently connected to
- We can set up a new network (such as a VPN or PPPoE connection)
- We can access the internet properties of the network adapter
- We can access the Sharing Settings
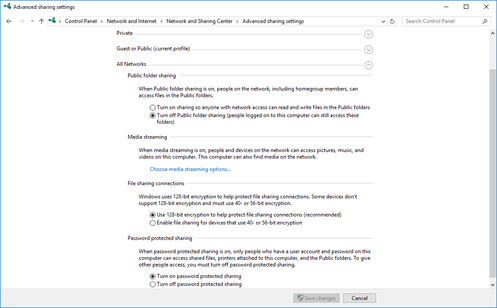
Sharing Settings
- Different sharing settings can be set for Private, Guest (Public) or All Networks
- Public Folder Sharing allows the computer to share folders with others on the network (others can only access folders whose permissions are set to “public”)
- File Sharing Connections allows us to choose whether to require 128-bit encryption in file sharing (more secure), or whether to allow 40 or 56-bit encryption (less secure, but allows access to more devices)
- Password Protected Sharing allows us to choose whether to require others to use a username/password to access shared files. The username/password must be set on the computer providing the shared files.
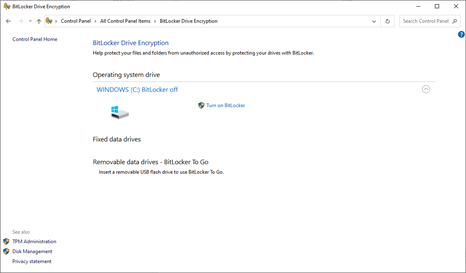
Control Panel – BitLocker
BitLocker encrypts the entire hard disk drive volume with an encryption key (a very long password). The key is stored to the hard disk drive and encrypted with your login password.
When you first activate BitLocker, the key is randomly generated
- You have the option to print the key, save it to OneDrive, or save it to USB
- If you forget your password, you must use the key to unlock your drive
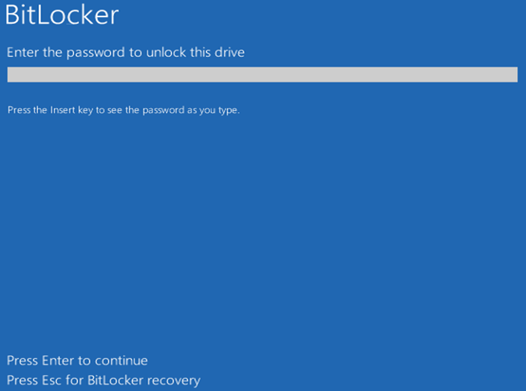
There are two modes
- User Authentication Mode
- The key is encrypted with your password and stored on the hard drive
- When you first activate BitLocker, the key is randomly generated
- To unlock the computer, you must enter your password
- BitLocker uses your password to decrypt the key
- BitLocker uses the key to decrypt files on the drive
- If you forget your password, you will be prompted to enter the key

- Transparent Mode
- The key is stored in the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) if your computer has one
- May also be stored in Active Directory (for Windows Domain users)
- You are not prompted for a key or a password when the computer boots
- The most basic parts of Windows are not encrypted
- When you boot your computer, Windows appears to load like normal (it loads the unencrypted files)
- The TPM verifies that the Windows files have not been modified, and knows that it can trust the Windows files
- You log in with your Windows password.
- If you enter the correct password, Windows authorizes the TPM to release the key, and decrypt the remaining files on the drive
- The key is stored in the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) if your computer has one
From the BitLocker menu you can see a list of available drives and whether BitLocker is enabled on each of them. You can also turn BitLocker on or off, suspend BitLocker, or back up the recovery key.
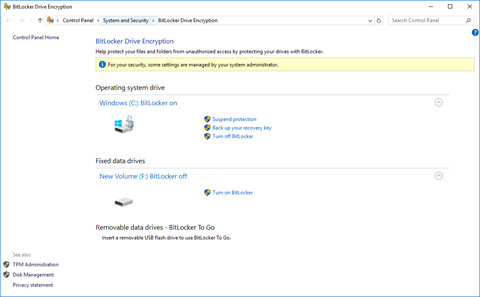
You can choose to allow Windows to automatically unlock the drive (through the TPM) or force it to require an additional password
When you set up BitLocker, choose where you want to save the recovery key
- Cloud account
- USB flash drive
- Save to a file
- Print the key
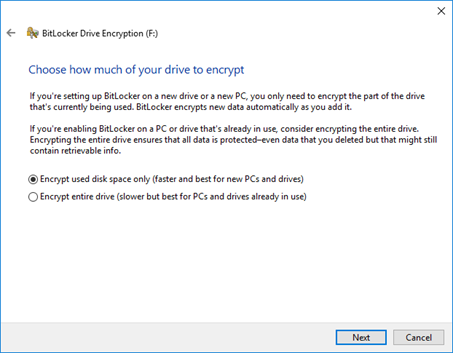
You can choose to encrypt used disk space (faster) or all disk space (more secure because it encrypts deleted data)
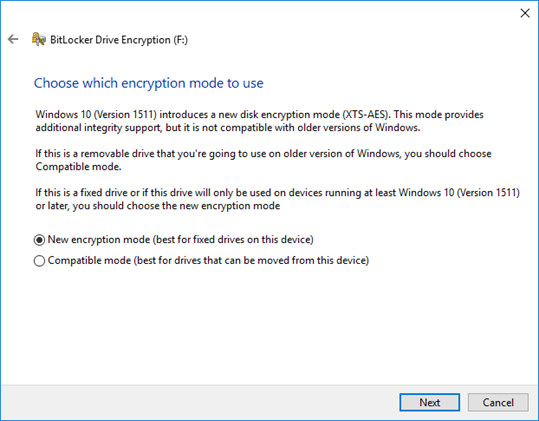
Choose the type of encryption mode that you want to use
- New encryption mode
- More stable; reduces the risk of losing your data
- Only compatible with Windows 10; if you’re encrypting a USB drive, don’t choose this option because previous versions of Windows won’t be able to decrypt it
- Compatible mode
- Less stable
- Compatible with older versions of Windows
After going through all these steps, Windows will encrypt the drive
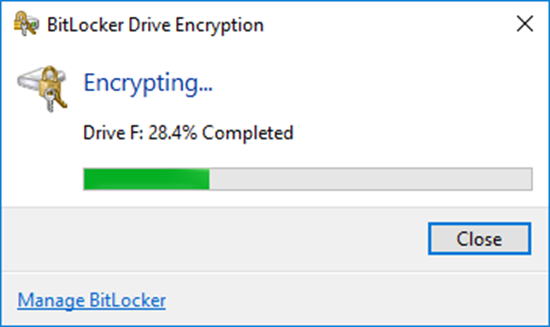
You can also access the BitLocker status from the command prompt
- Type manage-bde status
Mail Options
Mail Options allows us to set up new e-mail accounts and profiles. The settings only apply to Microsoft Outlook, and Microsoft Outlook must be installed for these settings to have any effect.
If you have a problem with Microsoft Outlook, you might go here to make changes to the Mail profile.
Indexing
Indexing helps make Windows searches faster. Windows builds an index of
- Emails stored by Microsoft Outlook
- User content
- Start menu
- Other items that you choose to index.
If you find that searches are slow, you can force Windows to reindex your information.
Ease of Access
The Ease of Access section makes your computer easier to use.
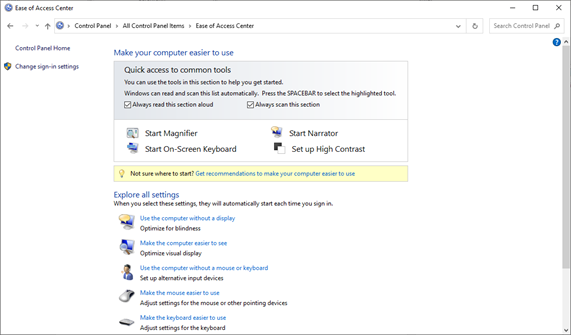
There are many settings
- Turn on a Narrator to read the items that you have your mouse over top
- Turn on Audio Descriptions. Audio Descriptions tell us what is happening in a video
- Turn on High Contrast in the display, which makes items easier to see
- Make the mouse pointer larger
- Turn on Sticky Keys. Sticky Keys allows Windows to “hold down” the CTRL, ALT or Shift keys when one is pressed. This means that you can enter a command like CTRL + ALT + DELETE without having to hold down the CTRL or ALT keys. You can press them one at a time.
- Allows you to see a visual notification when a sound is played
