3.6 Given a scenario, deploy and configure multifunction devices / printers and settings
- Properly Unboxing a Device – Setup Location Considerations
- Use Appropriate Drivers for a given (OS)
- Printer Control Language (PCL) vs PostScript
- Device Connectivity
- USB
- Ethernet
- Wireless
- Public/Shared Devices
- Printer Share
- Print Server
- Configuration Settings
- Duplex
- Orientation
- Tray Settings
- Quality
- Security
- User Authentication
- Badging
- Audit Logs
- Secured Prints
- Network Scan Services
- SMB
- Cloud Services
- Automatic Document Feeder (ADF) / Flatbed Scanner
Properly Unboxing a Device – Setup Location Considerations
The first step in installing a printer is to take it out of the box. Printers have many moving parts, but if they move during shipping, they will probably end up broken. The printer manufacturer does not want this to happen, so they add a lot of tape, Styrofoam, and cardboard. Each printer will come with a detailed instruction sheet, which tells you how to remove the packaging.
If the printer is large and heavy, then you might need help to take it out of the box.
You should think about where you are going to put the printer. If it is a network printer, shared by multiple people, then you should install it in a central location, near an ethernet port.
How to install a printer in Windows – USB
At home, the best practice is to do the following
- Plug the printer into the computer or onto your network
- Plug the printer into a USB port
- Plug the printer into an ethernet port
- Connect the printer to your Wi-Fi network
- Plug the printer into a USB port
- Go to the printer manufacturer’s website and download the latest software application compatible with your operating system
- Run the installation software
- The software should automatically detect and install the printer. The software may contain bloatware and annoying pop ups that tell you to buy more ink cartridges.
How to install a printer in Windows – Network/Corporate Environment
At in a corporate environment, the best practice is to do the following
- Plug the printer into an ethernet port
- Set a static IP address on the printer
- Go to Devices & Printers and choose to “Add a new Printer”
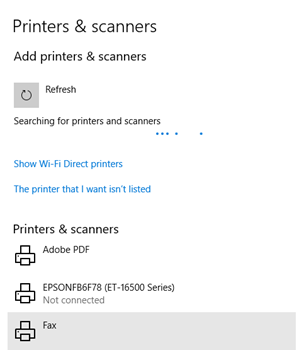
- Windows will automatically search for new printers (USB and network)
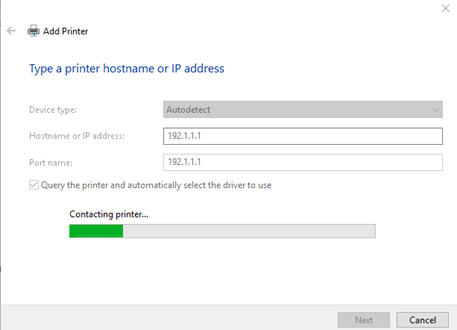
- Choose “The printer wasn’t listed”
- Enter the IP address of the printer
- Windows will connect to the printer and automatically select a driver
- In rare cases, Windows won’t be able to locate the correct driver
- Download the correct driver from the manufacturer’s website
- Choose “Have Disk” and select the driver that you downloaded
- Download the correct driver from the manufacturer’s website
- Windows will install the printer
- Give the printer a meaningful name
- In rare cases, Windows won’t be able to locate the correct driver
PCL vs Postscript
When you install a printer driver, you might have a choice between a PCL (Printer Control Language) or a Postscript driver. What is the difference?
PCL
- PCL is a language that tells the printer how to print a document
- It was developed by HP but in use by many manufacturers
- The current version is PCL 6
- When we print a document through a PCL driver, we are sending raw data (words, fonts, and the general layout of the document) to the printer. The printer generates and prints the document.
- Each printer model may generate a slightly different version of the document. What you see on your screen might not be exactly what comes out of the printer.
- PCL is faster because the document processing happens on the printer
Postscript
- Postscript is another language that tells the printer how to print a document
- Postscript was developed by Adobe but also in use by many manufacturers
- The Postscript language generates a detailed layout for the document and sends it to the printer. When you use Postscript, different printer models will output the same document. What you see on your screen is what you get from the printer.
- Postscript is slower because the computer must process the document.
Common Printer Settings
| Duplex | Duplex means printing on both sides of a sheet of paper The duplex setting saves paper A printer must have a component called a “duplexer” to do this A printer without a duplexer might allow you to choose “duplex” from the printer options. It will -print all the odd numbered pages -ask you to flip the sheets over and reinsert them into the printer -print the even numbered pages on the back of the sheets -this is annoying |
| Collate | When you print multiple copies of a document, the printer will print all the copies of each page at a time. For example, if you print five copies of a ten-page document, the printer will print five copies of the first page, then five copies of the second page, etc. until the end. When you choose to collate the document, it will print one copy of the document at a time. |
| Tray | A large printer can have several paper trays Each tray can contain a different size or quality of paper The printer might be able to detect what type of paper you put in each tray, but usually you must tell it When you print something, the printer chooses which paper tray to take the paper from You can also choose which paper tray the printer uses |
| Orientation | The orientation of the document can be Portrait or Landscape This is determined by Windows or in the software that created the document |
| Quality | You may be able to choose whether you want to print a document in high quality or low quality Lower quality printing is faster, and uses less toner/ink |
Device Sharing
How can we share a printer or other device?
| Wired – USB | We connect the printer to one PC (main PC) via a USB cable We can use Windows to share the printer with other devices on the network if the main PC is powered on. When the PC shuts off or is disconnected from the network, then other devices will not be able to see the printer. |
| Wired – Ethernet | We connect the printer to our network via an ethernet port. Any device on network can connect to the printer and print if it has permission |
| Wireless – Bluetooth | Any device in range and with Bluetooth capability can connect directly to the printer and print. Bluetooth is not common. |
| Wireless – 802.11 | The printer connects to network wirelessly Any device on our network can connect to the printer and print if it has permission |
| Infrastructure vs ad hoc | An infrastructure Wi-Fi connection is a connection between the printer and the Wi-Fi network. Other devices connect to the same Wi-Fi network and can access the printer. An ad hoc Wi-Fi network connection is a Wi-Fi connection between the printer and a computer. During the ad hoc connection, the printer and the computer won’t be connected to other networks. The ad hoc connection is established temporarily and only for the purpose of printing. |
| Integrated Printer Server | A print server accepts print jobs and queues them. An integrated print server is one that is part of the printer. Why do we need a print server? A printer may receive print jobs faster than it can print them. If it gets too many jobs, it will become overwhelmed and ignore them. A printer may receive print jobs but be low on necessary supplies (ink, toner, paper, staples, etc.) The printer won’t be able to print until supplies are restocked. For security reasons, a user may want to print a document to a shared printer, but not actually have it print until he or she is next to the printer. The server keeps the document secure until the user is physically present to receive it. |
| Cloud Printing/Remote Printing | A cloud printing application is installed on a computer that has a USB or network connection to a printer. This is known as the server. Other users who wish to print but who do not have access to the printer install the client version of the cloud printing application. When a user prints a document, the cloud print client sends the document over the internet to the cloud print server. The cloud print server prints the document. Google Cloud Print was a popular cloud printing app, that is now discontinued. PaperCut is a cloud printing app that is gaining popularity. |
| TCP/Bonjour/AirPrint | Bonjour is a service that allows Apple resources to find each other on the network. Resources include iTunes and printers. AirPrint allows an Apple device to wirelessly connect to an AirPrint-enabled printer or to a non-AirPrint-enabled printer that is connected to a Windows or Mac OS computer. |
Printer Security
There are over 1000 ways to hack a printer. Most people focus on securing their network and ignore all the cybersecurity risks associated with their printers. Do not be one of those people.
- Make sure that you install firmware updates when they become available
- Protect the printer configuration page from unauthorized access. Do not allow users to print reports or settings from the printer.
- Lock printer configuration settings from unauthorized users
- Change the default username and password if you can
- Disable remote printing
- Encrypt the printer hard disk. The hard disk will contain copies of printed documents. If the printer is stolen, and the drive is encrypted, nobody will be able to access the contents.
- Connect to the printer via https instead of http. Use a print driver that supports encryption.
- Replace old printers that use outdated technology.
- Use private printing
- Private printing sends the job to the printer, but doesn’t automatically print it
- The printer will “release” (print) the job only when the user arrives at the printer and logs in. Authentication can be via a
- Username/password (can authenticate via LDAP or Active Directory)
- PIN
- Access card/proximity card. You can connect a USB access card reader to many enterprise printers
- Username/password (can authenticate via LDAP or Active Directory)
- Private printing sends the job to the printer, but doesn’t automatically print it
- For highly sensitive printers, connect the printer only via USB and don’t share it. Turn off network connections on the printer.
- Maintain printer audit logs. The audit log tracks every job that is printed.
Scanning
When you scan a document, where does it go? There are a few choices
- E-mail. The printer generates a PDF of the document and e-mails it to you or to an e-mail address that you specify. The printer may be linked to your corporate address book. If it is, then you can select a destination from the directory. For scan to e-mail to work, you must configure SMTP settings on the printer.
Many e-mail service providers do not permit anonymous e-mails. You must usually configure a separate e-mail account for your scanner. - Network. You create a shared folder on a server or computer. When you scan a document, the printer generates a PDF and places it in the shared folder. This feature uses Server Message Block (SMB) technology. Anybody who has access to the shared folder can see the document.
- Cloud. The scan goes to a cloud storage location. Many printer manufacturers provide cloud scan services. If a manufacturer does, then their printer is automatically linked to the cloud service. You can log in to the cloud application and download the scanned document.
You must be careful with a cloud scan service because the cloud operator can see any document that you have scanned.
There are two types of scanners
- Flatbed Scanner. The flatbed scanner is a large glass surface that can scan a document.
- We can only scan one page at a time
- We can scan large documents
- We can scan documents that contains staples or paperclips. We can also scan documents that are part of books, bound, or coiled.
- We can only scan one page at a time

- Automatic Document Feeder (ADF). The ADF is an automatic scanner. We feed it a stack of papers and it automatically scans all of them, one after the other.
- We can scan up to 100 pages at a time
- We can’t scan large documents
- We can’t scan documents that contain staples or paperclips. We can’t scan books.
- The ADF may jam if the papers are crumpled or wrinkled.
- We can scan up to 100 pages at a time
A large multi-function printer may have both a flatbed scanner and an ADF. Below is a Xerox printer with a flatbed scanner and an ADF.

