4.9 Given a scenario, use remote access technologies.
- RDP
- VPN
- Virtual Network Computer (VNC)
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM)
- Microsoft Remote Assistance (MSRA)
- Third-party tools
- Screen-Sharing Software
- Video-Conferencing Software
- File Transfer Software
- Desktop Management Software
- Security Considerations of Each Access Method
Why are remote access tools necessary?
- We don’t always have physical access to the device. For example, we might need to access a server located in a far away data center.
- We have physical access to the device, but it is “headless”. For example, we have a rack full of servers, but none of them have monitors or keyboards. It’s easier to access the servers remotely from a laptop.
- It is more cost effective. It might be cheaper and faster to obtain remote access to a computer than to drive to the client. This is especially true when a help desk must support geographically diverse clients. For example, the help desk is in India, but the clients are located all over the United States.
- We need to multi-task. We want to work on many devices at the same time, and the devices are far apart.
What is RDP?
The RDP Connection uses Remote Desktop Protocol. It was developed by Microsoft and allows you to remotely connect to a Windows machine. RDP allows a Windows computer to connect to another Windows computer and see its desktop. If you install the xrdp package on a UNIX machine, you can connect to it via RDP.
The machine that you connect to must have RDP enabled (requires Windows Pro). The computer that initiates the connection can share its hard drives, printers, audio, and clipboard. That means I can copy something from my local computer and paste it on the remote computer. I can also print a document on my remote computer and have it come out of my local printer.
To access RDP, open the Remote Desktop Protocol dialog box and enter the IP address or hostname of the remote computer.
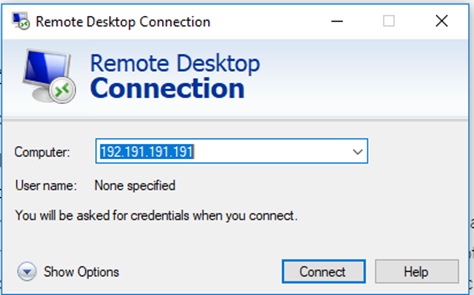
The remote computer will present you with a login prompt. You must enter your username and password to connect. The username and password must be configured on the remote computer, or the username and password must be configured on an Active Directory server of which the remote computer is a part of.
RDP uses TCP port 3389. The computer that you’re connecting to must permit remote connections
- To enable RDP connections on a remote computer, go to System Properties and choose the Remote tab
- You can choose to permit only specific users to connect via RDP
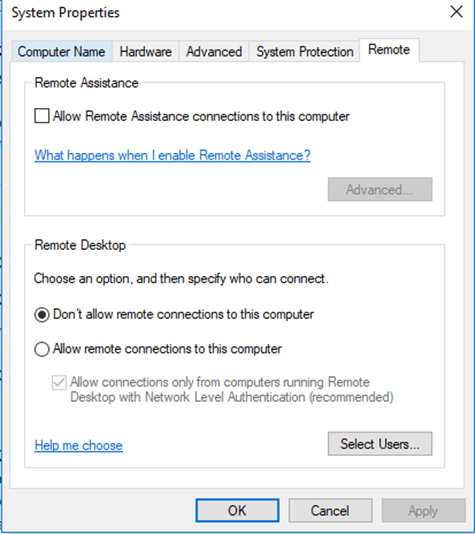
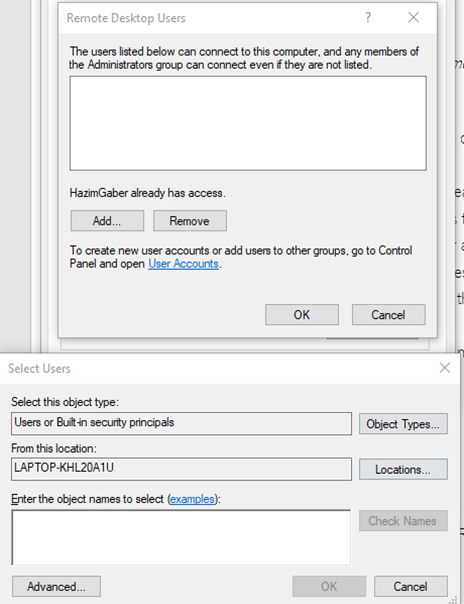
- You can choose which users are able to connect (Administrators have access by default)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
As mentioned previously, a VPN is a Virtual Private Network. It allows a remote user (working from home, a hotel, a hotspot, etc.) to connect to a corporate network through a tunnel. Essentially, the traffic from the user’s computer is packaged and sent through a tunnel to the corporate network. A VPN is good when a user needs to access multiple devices or resources on a network.
Virtual Network Computer (VNC)
VNC is a protocol like RDP. It allows a local device to view and control the screen of a remote device. VNC operates across many types of operating systems and hardware, and many implementations are open source. There are many applications that implement VNC.
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM)
RMM is a general term for a class of applications that can be used to remotely monitor and configure devices such as servers and network appliances. When choosing a remote management tool, think about
- How reliable the tool is
- How many different types of devices your tool can monitor. Do you need multiple tools to manage your devices, or can everything be managed under a “single pane of glass”?
- How much does the tool cost?
- How secure is the tool? Where does it store your data? Does it log all access attempts and activities? Does it support multi-factor authentication?
Microsoft Remote Assistance (MSRA)
Microsoft Remote Assistance, also known as Windows Remote Assistance or Quick Assist, is a tool that is based on RDP. It allows a local user to connect to a remote computer and provide help. The tool is built into all versions of Windows since Windows XP.
Unlike RDP, a remote user must manually allow the connection. Also, MSRA does not run with administrator privileges. If the local user chooses to run a task with administrative privileges, the remote user will be prompted to allow or deny the action.
Secure Shell (SSH)
SSH, or Secure Shell replaced Telnet. It is a tool to connect to a remote computer, specifically one that runs a UNIX operating system. SSH is command line based, but you can start a graphical user interface through SSH if you have the correct programs installed.
SSH authenticates the user so that only authorized users can access the resource, and authenticates the resource, so that the identify of the resource is confirmed to the user.
Server-based
Many servers have a hardware-based remote access system. For example, HP servers have iLO and Dell servers have iDRAC, which allow remote access to the server. The iLO/iDRAC card is a separate physical card that acts like “a mini server”. It allows you to manage the BIOS of server, reboot server, etc. iLO and iDRAC are more powerful than RDP because they allow you to stay connected while rebooting the server, modifying network settings, reinstalling the operating system, or changing hardware settings.
Third-party tools
There are many third-party tools that provide remote access. They include GoToMeeting, BeyondTrust (formerly Bomgar), TeamViewer, and LogMeIn.
Advantages of third-party tools
- You can collaborate with multiple support agents
- You can transfer a remote session to another, more experienced agent, or share the session with them
- You can record remote sessions
- You can execute special actions including CTRL+ALT+DEL or reboot the computer
- You can “pin” a client so that you can reconnect to it without having the user present
Disadvantages of third-party tools
- They can be expensive. Bomgar costs $2000+ per user per year; other programs are less expensive but have less features.
- Your data will travel through a third-party server, which could be a security risk (Bomgar sells an appliance that you can host yourself).
- It can be difficult to explain to a user how to download the remote software and establish a connection, whereas other applications (RDP and SSH) are built in.
Remote software can be divided into the following categories
- Screen-Sharing Software. Screen sharing applications allow you to view the screen of the remote computer. Examples include Team Viewer and AnyDesk.
- Video-Conferencing Software. Video conferencing software allow you to host a video call with multiple users. During the conference, a user can present the contents of his screen, and can give control to other users. An example is Microsoft Teams.
- File Transfer Software. File transfer software allows you to share files. The file transfer application may be cloud based in that you can upload a file and allow others to download it, or it may allow you to remotely access the hard disk drive of a remote computer.
- Desktop Management Software. Desktop management programs are used by administrators to remotely monitor and configure user computers.
Security Considerations for Remote Access
Before you set up remote access, think about the following
- Where possible, do not allow remote access directly from the internet. Force users to connect to a VPN. Once connected to a VPN, users can connect via a second remote application.
- Use RDP to connect to Windows machines and SSH to connect to UNIX machines. Never use Telnet.
- Use two-factor authentication to verify the identity of each person who connects and log all access attempts.
- Users should have access to only the specific devices that they need to do their jobs. Users should not have administrator level access unless necessary.
- Do not allow users to install third-party remote desktop applications such as Team Viewer
- When using a third-party monitoring tool, ensure that it is configured to store data on your local server.
- Instruct users to exercise caution when sharing content on a video call. A user should share an “application” such as a PowerPoint presentation, and not their entire computer screen.
